We are striving for environmental conservation based on the ISO 14001 environmental management system.
As a result, we have so far achieved the reduction of the usage of various types of energies, improvement of the per-unit consumption of these energies, reduction of waste, etc. In FY2023, compared to FY2022, the usage of electricity and thermal energy decreased, partly due to the closure of the thermosetting molding materials department at the Nobeoka Factory.
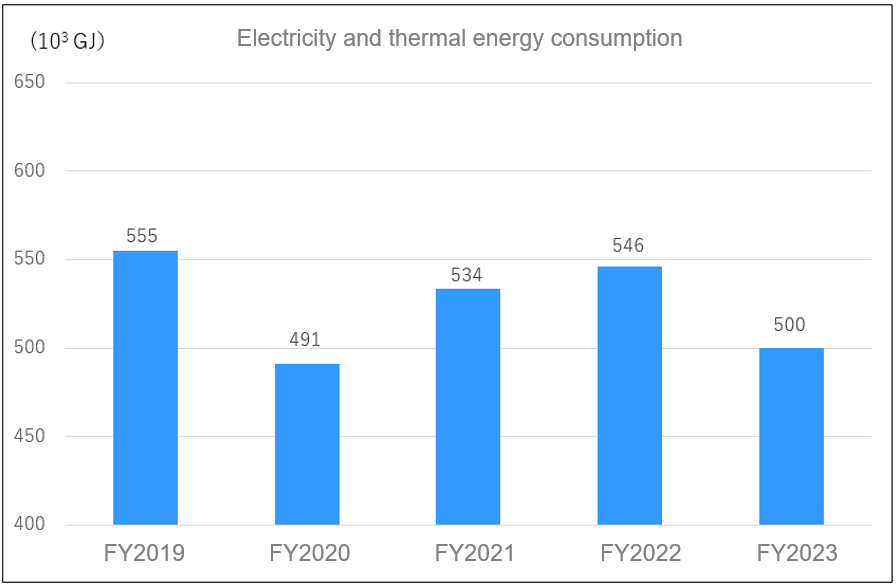
(1)Energy consumption - Electricity and thermal energy consumption
Electricity and thermal energy consumption
The usage of electricity and thermal energy at each of our factories, as calculated in accordance with the Act on the Rational Use of Energy, was 500,000 GJ, a decrease of about 46,000 GJ (8.5%) compared to the last year.
*) Energy consumption is converted to GJ using a conversion factor.
Energy consumption for freight transportation
The energy usage for freight transportation at each of our factories, calculated based on the Act on the Rational Use of Energy, was about 70.3 thousand GJ, a decrease of 3.4 thousand GJ (4.6%) compared to last year.
*) Energy consumption is converted to GJ using a conversion factor.
(2)Energy conservation and prevention of global warming
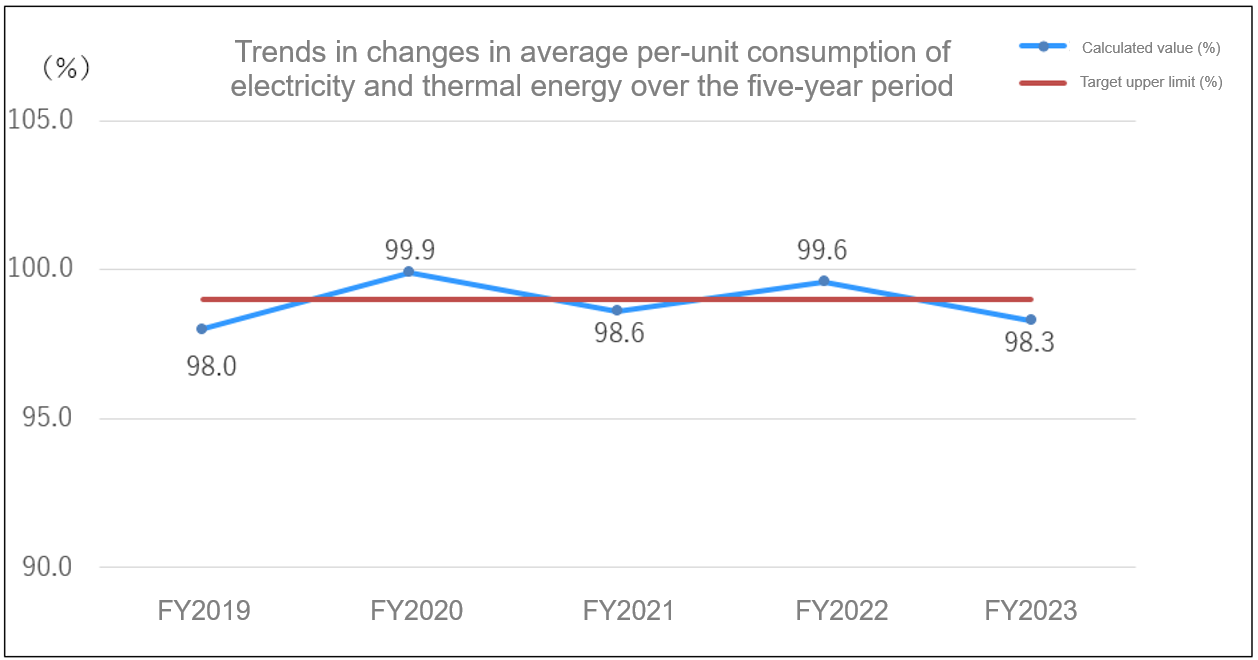
Reduction of the per-unit consumption of electricity and thermal energy
We have been designated as a “specified business operator” under the Act on the Rational Use of Energy and the Promotion of Non-Fossil Energy (the "Act on the Rational Use of Energy"), and submits a medium- to long-term plan and regular reports on the use of electricity and thermal energy to the Kyushu Bureau of Economy, Trade and Industry every year.
The specified business operators are required to make efforts to reduce their per-unit energy consumption at least 1% compared to the previous year, and to reduce their annual average energy consumption at least 1% over the medium to long term.
The per-unit consumption for FY2023 decreased by 2.5% compared to the previous year, and the average per-unit consumption change over the five-year period was also 1.7% lower than in FY2022, so the target of at least 1% reduction was achieved. We have been systematically investing in energy-saving measures, and in FY2023 we are also working to improve energy efficiency by introducing energy-saving equipment such as injection molding machines, and we have achieved the target due in part to the closure of our thermosetting molding materials department.
In FY2024, we will continue to strive for improvement of the efficiency of our consumption of electricity and thermal energy so that we can fulfill the effort obligations imposed on specified business operators under the Act on the Rational Use of Energy.
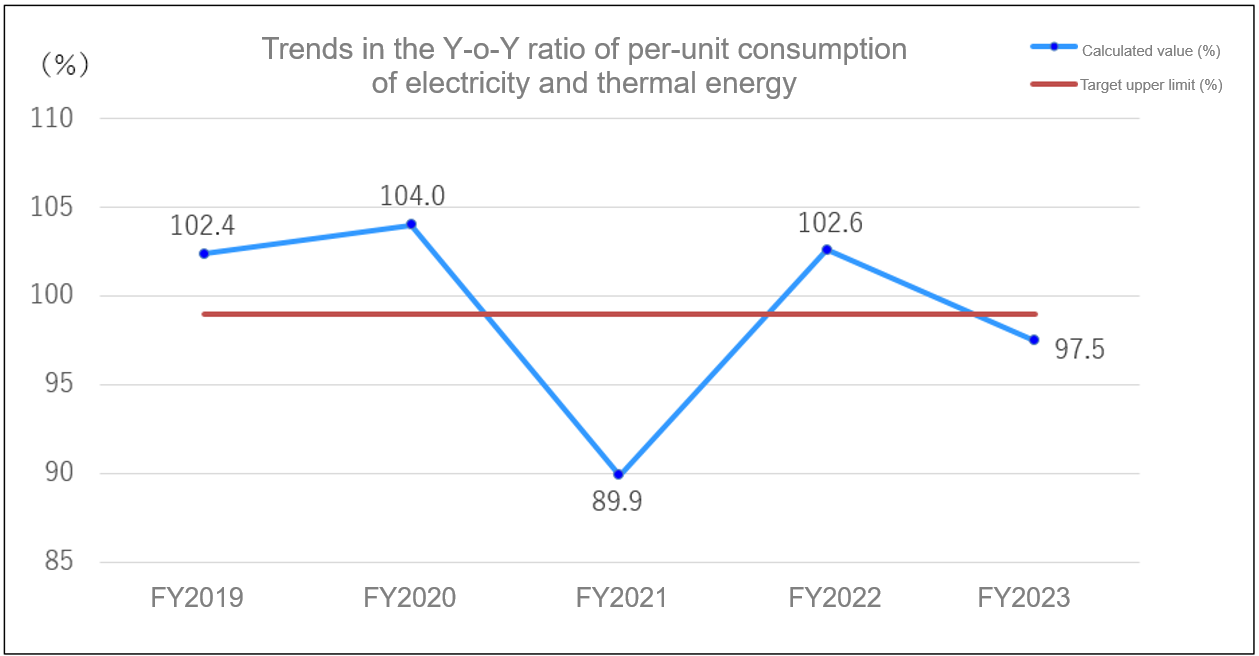
Reduction of per-unit energy consumption in freight transportation
We have been designated as a “specified shipper” under the Act on the Rational Use of Energy, and submit a medium- to long-term plan and regular reports on the use of energy for freight transportation to the Kyushu Bureau of Economy, Trade and Industry every year.
The specified shippers are required to make efforts to reduce their per-unit energy consumption for freight transportation at least 1% compared to the previous year, and to reduce their annual average energy consumption at least 1% over the medium to long term.
The per-unit consumption for FY2023 increased by 0.6% compared to the previous year, and the average per-unit consumption change over the five-year period decreased by 0.6%, and both failed to achieve the target of reducing by 1% or less. The reason for this is mainly due to the increase in the ratio of products with high per-unit energy consumption for transportation as a result of the decrease in production volume. We have strived to improve loading rates, increase the size of our delivery vehicles, and switch to JR transportation, but in FY2024, we will endeavor to further improve logistics efficiency so that we can fulfill the effort obligations imposed on specified shippers under the Act on the Rational Use of Energy.

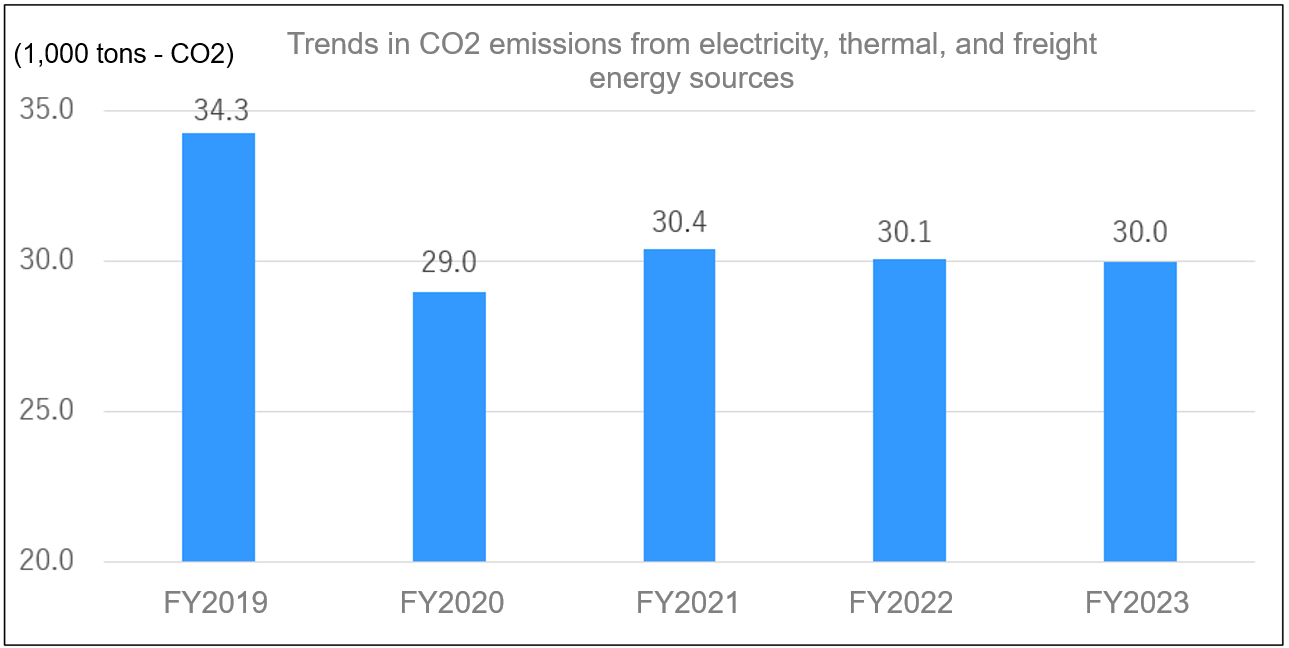
Reduction of CO2 emissions from energy sources for electricity, thermal and freight transportation
Under the Act on the Rational Use of Energy, our energy-derived CO2 emissions from electricity, thermal, and freight transportation in FY2023 were 30.0 thousand tons of CO2, and 0.2% decrease compared to FY2022.
The implementation of proactive energy-saving activities, including the conversion of fuel used for equipment, change to high-efficiency equipment, shift to electricity with a low CO2 emission coefficient, and the streamlining of logistics, which we have been working on, has contributed to a slight reduction in CO2 emissions. However, the CO2 emissions only decreased slightly because the emission factor for converting the amount of electricity from power companies into CO2 emissions increased in FY2023 compared to FY2022 (e.g. Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc. increased by 38%),
Prevention of CFC leakage
We have been striving to prevent the leakage of CFCs by complying with the CFC Emission Control Act, including thorough inspection and maintenance of CFC equipment and thorough recovery at the time of disposal, and by promoting the use of non-CFC equipment, such as control panel coolers.
(3)Environmental conservation
Emission and transfer of designated chemical substances and measures to reduce them
We have reduced the emissions and transfer of chemical substances designated by the Act for the Promotion of Chemical Substance Management by 9.9% in FY2023 compared to FY2022.
We have been promoting the reduction of waste containing raw materials that contain designated chemical substances, and we will continue to properly manage designated chemical substances and strive to reduce their emissions and transfer.
※ Act for the Promotion of Chemical Substance Management: Act on the Promotion of the Improvement of Management and the Grasp of the Amount of Release of Specific Chemical Substances into the Environment
Designated chemical substances we manage based on PRTR
| Factory |
Names of the specified chemical substances |
| Nobeoka Factory |
Organotin compounds, lead and its compounds, antimony and its compounds, hexamethylenetetramine, phenol, dicyclopentadiene, methylenebis(4,1-phenylene)diisocyanate |
| Aichi Factory |
Zinc water-soluble compounds, bisphenol A, epichlorohydrin, 2,4-xylenol, 2,6-xylenol, xylene, cumene, glyoxal, cresol, 1,4-dioxane, N,N-dimethyl formamide, hexamethylenetetramine, tetraethylenepentamine, triethylamine, 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene, 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene, naphthalene, phenol, formaldehyde, methylnaphthalene, methylenebis(4,1-phenylene), trinormalbutyl phosphate, lead compounds, 2-ethylhexanoic acid, caprolactam, manganese acetate, dioxins, DMF |
| Tochigi Factory |
Hexamethylenetetramine, organotin compounds, lead and its compounds, dioxins |
| Hiroshima Factory |
Hexamethylenetetramine, dioxins |
*) PRTR is a system for grasping, compiling and publishing data on the amount of chemical substances specified by the PRTR Law (Law concerning Reporting etc. of Release of Specific Chemical Substances to the Environment and Promotion of the Improvement of Their Management) that have been released into the environment from what kind of sources, or that have been contained in waste and transported outside of factories.
Total emissions of industrial waste
Based on the 4Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle, and resource recovery), which are typical activities for reducing industrial waste, we are promoting the reduction of total industrial waste emissions, the effective use of generated industrial waste, and the reduction of industrial waste disposed of simply (landfill) from the total emissions (zero emissions).
The total emissions in FY2023 was 17.1 thousand tons, an increase of 1.2% compared to FY2022.
We will continue to further reduce waste emissions.
Simple disposal (landfill) as a proportion of the total industrial waste emissions
Simple (landfill) disposal in FY2023 increased by 11.9% compared to FY2022, and the simple disposal rate (the ratio of simple waste disposal of by simple disposal to the total industrial waste emissions) also increased by 10.5%.
Main activities to promote the reduction of simple (landfill) disposal, etc. are as follows.
ー Thorough implementation of the 4Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle, and resource recovery)
ー Converting industrial waste into valuable resources by separation
ー Exploring needs for effective use in the marketplace
Furthermore, we will strive to reduce the simple disposal rate, which has a large environmental impact, to 1% or less in the future.
%20disposal%20and%20its%20ratio%20to.png)
Preservation of water resources
The water used at ASAHI YUKIZAI's factories etc. includes industrial water, groundwater and tap water.
The water usage in FY2023 decreased by 3.7% compared to FY2022.
The main use of water is for cooling manufacturing equipment, so water usage depends on production volume, but we are striving to reduce water usage through recycling, reuse, and other measures. We will continue to strive for efficient use and promote the preservation of water resources.